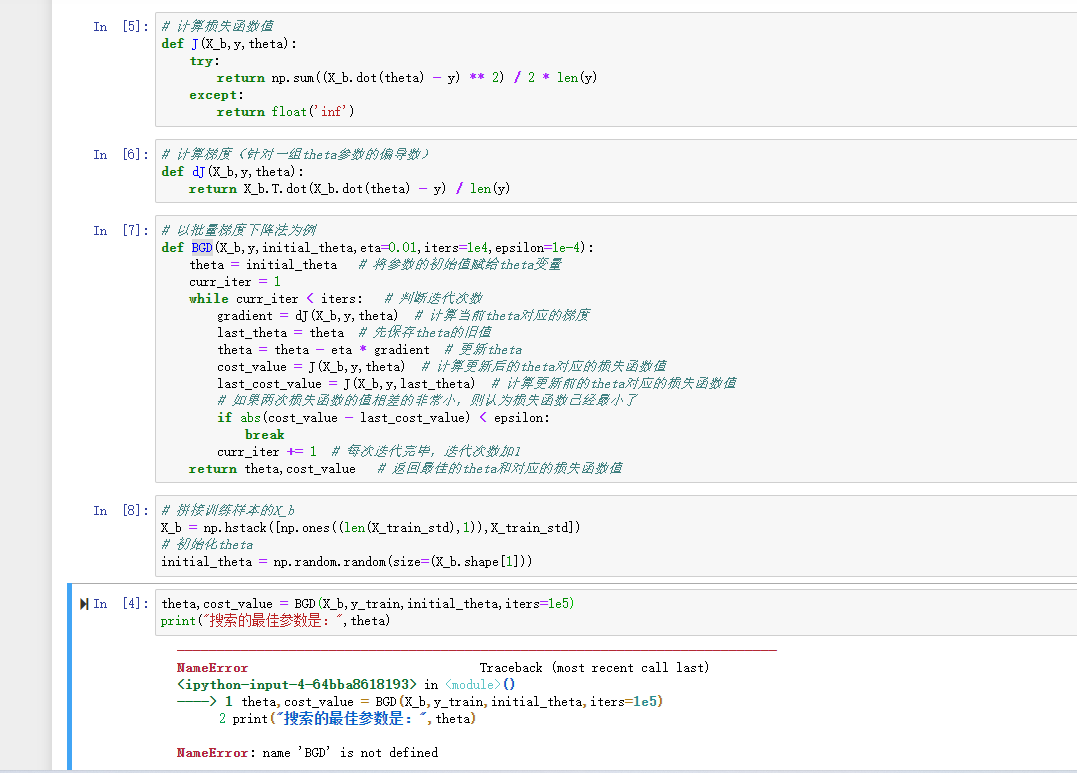
# 以批量梯度下降法为例
def BGD(X_b,y,initial_theta,eta=0.01,iters=1e4,epsilon=1e-4):
theta = initial_theta # 将参数的初始值赋给theta变量
curr_iter = 1
while curr_iter < iters: # 判断迭代次数
gradient = dJ(X_b,y,theta) # 计算当前theta对应的梯度
last_theta = theta # 先保存theta的旧值
theta = theta - eta * gradient # 更新theta
cost_value = J(X_b,y,theta) # 计算更新后的theta对应的损失函数值
last_cost_value = J(X_b,y,last_theta) # 计算更新前的theta对应的损失函数值
# 如果两次损失函数的值相差的非常小,则认为损失函数已经最小了
if abs(cost_value - last_cost_value) < epsilon:
break
curr_iter += 1 # 每次迭代完毕,迭代次数加1
return theta,cost_value # 返回最佳的theta和对应的损失函数值
# 拼接训练样本的X_b
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(X_train_std),1)),X_train_std])
# 初始化theta
initial_theta = np.random.random(size=(X_b.shape[1]))
theta,cost_value = BGD(X_b,y_train,initial_theta,iters=1e5)
print("搜索的最佳参数是:",theta)